Manufacturing (excludes F&B), Creative and ICT:
On this page
Summary
- Japan has set a government target to double its domestic space market from JPY 4 trillion (NZD 43 billion) in 2020 to JPY 8 trillion (NZD 87 billion) by the early 2030s. The Japanese government is setting up a number of programmes and initiatives, with the aim of expanding its space sector ecosystem to include not just its traditional, well-established big players but also more startups. While overseas entities are not directly eligible for Japan’s government funding, growth in Japan’s private sector presents commercial opportunities for New Zealand space sector companies to become partners with Japanese companies and form part of the wider supply chain.
Report
Overview of Japan’s space sector
Two keywords underpin Japan’s approach: “indispensability” and “autonomy”. Japan aims to develop and maintain a technological edge in key areas and also possess the ability to carry out necessary space activities on its own. Japan outlined these aims in its Basic Plan on Space Policy (adopted June 2023), which includes a target to double its domestic space market from JPY 4 trillion (NZD 43 billion) in 2020 to JPY 8 trillion (NZD 87 billion) by the early 2030s.
Japan's growing private sector
| Segments | Companies |
| Satellite data/ Space tech application | DigitalBlast, Synspective, Tenchijin, Yamap |
| Launch services | Innovative Space Carrier, Interstellar Technologies, MJOLNIR SPACEWORKS, SPACE ONE |
| Satellite infrastructure deployment and operation | ArkEdge Space, Axelspace, Infostellar, iQPS, Pale Blue, Space Compass, Synspective |
| In-orbit services | Astroscale, BULL, ElevationSpace, Space quarters, SpaceBD |
| Space tourism/ migration | ONETABLE, Yspace |
| Space exploration/ space mining | Ispace |
- JAPAN's SPACE INDUSTRY | JAXA Business Development and Industrial Relations Department(external link)
- SPACE COMPANY | JAXA Business Development and Industrial Relations Department(external link)
- Cross U signed preliminary agreements with three leading organisations in the European space industry – the European Space Agency, National Centre for Space Studies (CNES), and Harwell Science and Innovation Campus – to encourage cooperation across the space sectors in EU and Japan (Nov 2024)
- Synspective signed a deal for 10 Electron launches with Rocket Lab (Jun 2024)
- Astroscale launched world’s first debris inspection spacecraft, ADRAS-J, from Rocket Lab’s Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand
- ispace signed MOUs with mu Space towards future lunar orbiting missions (Feb 2024)
Government budget
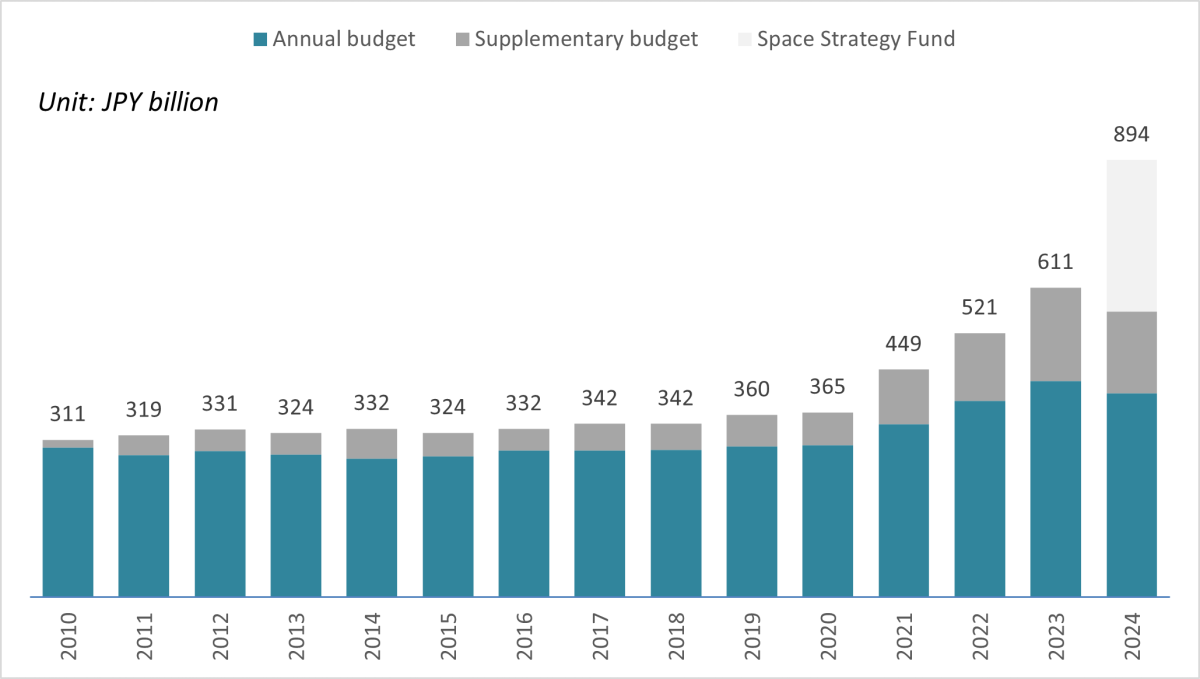
The supplementary budget approved in a given fiscal year is reflected in the chart above in the following fiscal year. (For example, the supplementary budget approved in FY2023 is reflected in FY2024 in the chart above.)
The Space Strategy Fund was included in the FY2023 supplementary budget.
Japan’s space technology strategy
- Space transportation – Enhanced space transportation capabilities, lower space transportation prices, higher launch frequencies, and meeting diverse space transportation needs.
- Systems technology
- Structural technology
- Propulsion technology
- Other core technology
- Transport services technology
- Launchpad and spaceport technology
- Satellites etc. – Disaster prevention and mitigation, solving global issues including national land resilience and climate change, creating innovation in the private sector, achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals, realising Society 5.0.
- Communications
- Satellite measurement system
- Remote sensing
- Orbital services
- Satellite infrastructure technology
- Space exploration – To create common human knowledge on the origins of the universe and the possibility of life on other planets, to expand the domain of human activities into deep space beyond the Moon, and to promote industry in lunar exploration and low Earth orbit activities.
- Astrophysics
- Solar system science/exploration
- Lunar exploration/development etc.
- Low earth orbit/international space exploration
- Cross-area/sector technologies – Continuous development of technologies common to the above-mentioned satellite, space science and exploration and space transportation sectors is essential to ensure supply chain autonomy and strengthen international competitiveness.
- Hardware technology to support advanced functional performance and flexibility (e.g. digital devices)
- Core mechanical technology to reduce size and weight while increasing mission sophistication (e.g. 3D printing)
- Core software technology to support increasing mission sophistication and flexibility (e.g. AI, machine learning)
- Transformation of development and manufacturing processes and supply chains that contribute to faster development cycles and mass production
- High-precision co-operative operation technology for multiple spacecrafts
Ongoing government-led initiatives
Space Strategy Fund
- Double the domestic space market from 4 trillion yen in 2020 to 8 trillion by the early 2030s
- Contribute to finding solutions for global, societal issues using space
- Cultivate knowledge of space and strengthen core technological capabilities
The three focus areas correspond with those outlined in the Space Technology Strategy:
- Space transportation
- Satellites etc.
- Space exploration
Small/Startup Business Innovation Research (SBIR) Programme
- Development and demonstration of launch vehicles in the private sector (MEXT)
- Development and demonstration of technology necessary for reducing space debris (MEXT)
- Development and demonstration of a lunar lander (METI)
- Demonstration of increased sophistication of satellite remote sensing business (METI)
Appendices
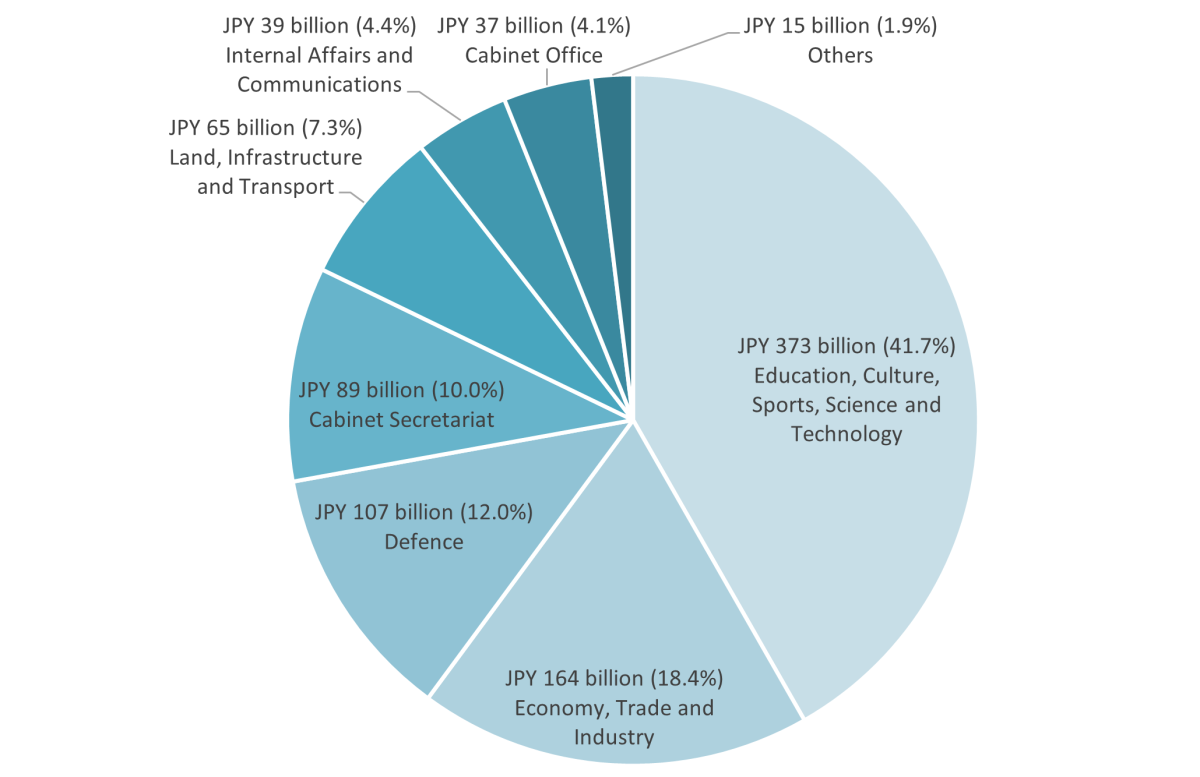
| Government agency | Project/ programme | Funding amount (JPY billion) |
| Ministry of Education, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) |
|
150 26 26 11 11 |
| Total: 373 | ||
| Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) |
|
126 19 |
|
Total: 164 |
||
| Ministry of Defence (MOD) |
|
23 12 |
|
Total: 107 |
||
| Cabinet Secretariat |
|
89 |
| Total: 89 | ||
| Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT) |
|
21 |
| Total: 65 | ||
| Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communication (MIC) | Space Strategy Fund Development of 10 Gbps-class high-speed optical transmission technology |
24 <30 |
| Total: 39 | ||
| Cabinet office | Development, servicing and operation of Quasi Zenith Satellite System(external link) |
24 12 |
| Total: 37 |
More reports
View full list of market reports(external link)
If you would like to request a topic for reporting please email exports@mfat.net
Sign up for email alerts
To get email alerts when new reports are published, go to our subscription page(external link)
Learn more about exporting to this market
New Zealand Trade & Enterprise’s comprehensive market guides(external link) export regulations, business culture, market-entry strategies and more.
Disclaimer
This information released in this report aligns with the provisions of the Official Information Act 1982. The opinions and analysis expressed in this report are the author’s own and do not necessarily reflect the views or official policy position of the New Zealand Government. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade and the New Zealand Government take no responsibility for the accuracy of this report.
Copyright
Crown copyright ©. Website copyright statement is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International licence(external link). In essence, you are free to copy, distribute and adapt the work, as long as you attribute the work to the Crown and abide by the other licence terms.

